Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kawaguchi, Koichi; Segawa, Tomoomi; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Makino, Takayoshi; Iso, Hidetoshi; Ishii, Katsunori
no journal, ,
The reworking of out of specification pellets is required for the effective use of nuclear fuel material and for reduction of the plutonium inventory in fuel fabrication facilities. It is known that the sintering density of mixed oxide pellets can be controlled without a pore-former by controlling the amount and particle size of the recovered powder in the raw powder. The collision plate type jet mill was separated into the classifier and the mill chamber, and these modules were used independently. The peak position shifted to smaller sizes gradually over the five cycles of classification and pulverization. The collision plate type jet mill is a promising form of equipment to obtain particles with objective sizes as the main component of a powder.

Tsuchimochi, Ryota; Kato, Masato; Hirooka, Shun; Matsumoto, Taku; White, J.*; McClellan, K.*
no journal, ,
High temperature XRD, Thermal expansion measurement, sound speeds measurement and DSC measurement of CaF were carried out. We confirmed that the specific heat of CaF
were carried out. We confirmed that the specific heat of CaF explicity shows the effect of Frenkel defect formation on top of the heat capacity at constant volume and dilatational term. The analysis of the specific heat will be discussed together with the measured data.
explicity shows the effect of Frenkel defect formation on top of the heat capacity at constant volume and dilatational term. The analysis of the specific heat will be discussed together with the measured data.
Segawa, Tomoomi; Kawaguchi, Koichi; Ishii, Katsunori; Fukasawa, Tomonori*; Fukui, Kunihiro*
no journal, ,
In the conversion process, a mixed solution of plutonium nitrate and uranyl nitrate recovered from spent fuel is converted into mixed oxide through microwave heating. Both, improvements in heating efficiency and powder characteristics, are important in microwave heating denitration. This study aims to advance microwave heating denitration. Thus, we investigated the effects of heating conditions when using an adiabator and the temperature rising rate of the particle characteristics of a uranium trioxide (UO ) powder synthesized from uranyl nitrate solutions through microwave heating. The temperature rising rate significantly increased when the adiabator was used compared to when not used at the same microwave power. The mass median diameters of the UO
) powder synthesized from uranyl nitrate solutions through microwave heating. The temperature rising rate significantly increased when the adiabator was used compared to when not used at the same microwave power. The mass median diameters of the UO powders decreased with the increasing temperature rising rate with and without using the adiabator. Heating conditions can control the particle characteristics of UO
powders decreased with the increasing temperature rising rate with and without using the adiabator. Heating conditions can control the particle characteristics of UO powders.
powders.
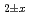
Kato, Masato; Watanabe, Masashi
no journal, ,
Uranium di-oxide (UO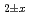 ) is nonstoichiometric compound, and the stoichiometry significantly affects thermal properties. Therefore, oxygen chemical potential is one of important thermodynamic data to evaluate phase stability and to know properties. Many researches have measured oxygen chemical potential as functions of temperature and oxygen-to-uranium (O/U). However, it is difficult to derive correlation equation to represent the oxygen potential because of large uncertainty in measurement data and complicated mechanism. In this report, the oxygen chemical potential was determined by gas equilibrium method, the defect equilibria was evaluated, and the correlation equation was derived.
) is nonstoichiometric compound, and the stoichiometry significantly affects thermal properties. Therefore, oxygen chemical potential is one of important thermodynamic data to evaluate phase stability and to know properties. Many researches have measured oxygen chemical potential as functions of temperature and oxygen-to-uranium (O/U). However, it is difficult to derive correlation equation to represent the oxygen potential because of large uncertainty in measurement data and complicated mechanism. In this report, the oxygen chemical potential was determined by gas equilibrium method, the defect equilibria was evaluated, and the correlation equation was derived.
 granules produced using wet granulator
granules produced using wet granulatorIshii, Katsunori; Segawa, Tomoomi; Kawaguchi, Koichi
no journal, ,
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is developing a simplified mixed oxide (MOX) fuel fabrication process. In this process, a wet granulator improves the flowability of MOX raw powder for the pelletizing process 1, 2). Following this granulation step, the formed granules have moisture content of approximately 10 wt.%. To adhere to the acceptance standards regarding moisture content for the fuel pellet fabrication step, drying the granules under the moisture content of 1 wt.% using a dryer is necessary. To maintain the granule shape during powder handling and shaker process of a pressing machine, the granules must be adjusted to enough crushing strength. However, the relation between dry conditions and granule crushing strength has not been reported. Therefore, to estimate the appropriate heating conditions of the dryer, we investigated the influence of varying heating conditions on moisture content and granule crushing strength.
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Shirasu, Noriko; Saito, Hiroaki
no journal, ,
The FEMAXI-ATF code has been developed to analyze the SiC-cladding-fuel behaviors as an extended version of the LWR fuel-analysis code FEMAXI-7. The analysis using the FEMAXI-ATF code indicated that the SiC cladding shows large swelling by irradiation and it causes the decrease of cladding thermal conductivity and the gap conductance, and consequently increase of the fuel temperature. Furthermore, the mechanical integrity for SiC cladding and influence of pellet-cladding mechanical interaction (PCMI) were evaluated.

Watanabe, Masashi; Tanaka, Kosuke; Kato, Masato
no journal, ,
In this study, the shrinkage behavior of CeO , which is widely used in surrogate material of the nuclear fuel, were studied using a thermomechanical analyzer in various oxygen partial pressure, to discuss the sintering mechanisms under the low oxygen potentials. The shrinkage ratios were significantly different between the air atmosphere and the oxygen partial pressure controlled atmosphere. The shrinkage began at lower temperature with increasing P
, which is widely used in surrogate material of the nuclear fuel, were studied using a thermomechanical analyzer in various oxygen partial pressure, to discuss the sintering mechanisms under the low oxygen potentials. The shrinkage ratios were significantly different between the air atmosphere and the oxygen partial pressure controlled atmosphere. The shrinkage began at lower temperature with increasing P /P
/P ratio. The relationship between P
ratio. The relationship between P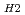 /P
/P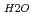 ratio and shrinkage ratio in the sintering process of PuO
ratio and shrinkage ratio in the sintering process of PuO is similar to the result of this study. Therefore, it seems that both have the same sintering mechanism.
is similar to the result of this study. Therefore, it seems that both have the same sintering mechanism.

Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ogasawara, Masahiro*
no journal, ,
The heat capacity of MOX fuel is one of the important thermophysical properties. To evaluate the heat capacity of MOX fuel, the heat capacity of PuO is required because the heat capacity of MOX fuel is generally calculated from the compositional average of those of UO
is required because the heat capacity of MOX fuel is generally calculated from the compositional average of those of UO and PuO
and PuO . The experimental results of the heat capacity of PuO
. The experimental results of the heat capacity of PuO are very scarce. In this study, the enthalpy of PuO
are very scarce. In this study, the enthalpy of PuO pellet was measured in the temperature range from 980 to 2160 K with a drop calorimeter. In the measurement, the pellet was loaded in a tungsten container and a rhenium inner container was applied to prevent the reaction between the specimen and the tungsten container. It was found that the enthalpy increased at a constant rate with increasing temperature up to about 1900 K, and that above about 1900 K, its rate tended to increase with increasing temperature. It means that the heat capacity is raised when temperature exceeds about 1900 K.
pellet was measured in the temperature range from 980 to 2160 K with a drop calorimeter. In the measurement, the pellet was loaded in a tungsten container and a rhenium inner container was applied to prevent the reaction between the specimen and the tungsten container. It was found that the enthalpy increased at a constant rate with increasing temperature up to about 1900 K, and that above about 1900 K, its rate tended to increase with increasing temperature. It means that the heat capacity is raised when temperature exceeds about 1900 K.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
This paper introduces the nanoscale structural analysis of ferroelectrics obtained using synchrotron radiation high-energy X-ray diffraction experiments. In particular, we report the results of local structure analysis of the structure of crystalline materials with lack of translational symmetry, those are relaxor ferroelectrics and ferroelectric nanocrystals, by using the atomic pair-distribution function.
Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.*; Aizawa, Kazuya
no journal, ,